EFFECTIVENESS OF PARTICLE DAMPERS IN BUILDINGS SUBJECTED TO NARROW-BAND SEISMIC EXCITATIONS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18867/ris.113.617Keywords:
structures with particle dampers, narrow-band seismic excitations, displacement demand, Mexico City earthquakesAbstract
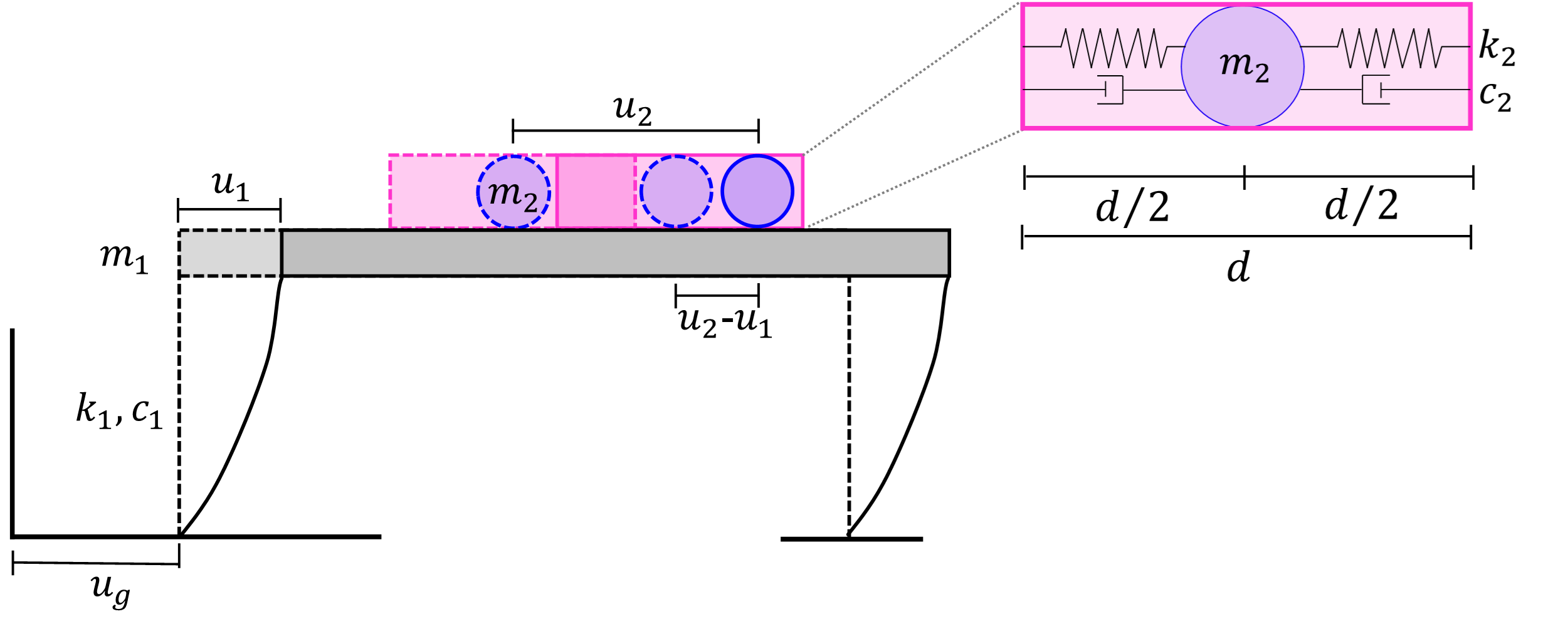
This numerical study evaluates the effectiveness of Particle Dampers (PDs) on buildings, which are capable of reducing the lateral response of the primary structural system when subjected to narrow-band seismic excitations. First, the seismic response for maximum displacement of a single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) system was studied for three configurations, namely: 1) a SDOF system without damper; 2) a SDOF system with Tuned Mass Damper (TMD) and 3) a SDOF system with PD. Then, the response of 11-storey and 17-storey three-bay linear frames with PD, TMD and without them are analyzed under narrow-band seismic motions. Results indicated that the main advantage of a PD is the significant reduction of floor accelerations and lateral displacements when the ratio between the predominant frequency of the ground earthquake excitation and the predominant frequency of the building is close to unity and the first mode of the frame becomes dominant. It is essential to carry out an experimental validation and contrast of these findings, so that engineers can consider the feasibility of implementing PDs in structures exposed to narrow-band seismic excitations, as is the case in Mexico City.
Downloads
References
Bryce, L.F., Eric, M.F. y Steven, E.O. (2000). Effectiveness and predictability of particle damping, Proceedings of the SPIE's 7th Annual International Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials, International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Butcher, J. C. (2016). Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations. John Wiley and Sons.
Campbell, R. (1995). A true tall tale about the Hancock Tower, Boston Globe. 3.
Chopra, A. K. (2012). Dynamics of Structures: Theory and Applications to Earthquake Engineering (4th ed.). Prentice Hall.
Den Hartog, J. P. (1947). The Undamped and Damped Dynamic Vibration Absorbers. Mechanical Vibrations, 3, 112-113.
Esteva, L. (1993). Respuesta sísmica de cortante con osciladores resonantes Parte I. Funciones de amplificación dinámica. Informe al DDF. Instituto de Ingeniería UNAM, Proyecto 3521.
Ghorbani-Tanha, A.K., Noorzad, A. y Rahimian, M. (2009). Mitigation of wind-induced motion of Milad Tower by tuned mass damper, Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build., 18(4), 371-385. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/tal.421
Hu, L., Huang, Q.B. y Liu, Z.X. (2008). A non-obstructive particle damping model of DEM, Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des., 4(1), 45-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-007-9053-z
Inoue, M., Yokomichi, I., y Hiraki, K. (2011). Particle damping with granular materials for multi degree of freedom system. Shock and vibration, 18(1-2), 245-256. DOI: 10.3233/SAV-2010-0611
Jerome, J. C. (2002). Introduction to structural motion control. Prentice Hall Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, 7458, 217-285.
Li, K., y Darby, A. P. (2006). Experiments on the effect of an impact damper on a multiple-degree-of-freedom system. Journal of Vibration and Control, 12(5), 445-464. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1077546306063504
Lu, X. y Chen, J. (2011a). Mitigation of wind-induced response of Shanghai Center Tower by tuned mass damper, Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build., 20(4), 435-452. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.659
Lu, X. y Chen, J. (2011b). Parameter optimization and structural design of tuned mass damper for shanghai centre tower, Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build., 20(4), 453-471. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.649
Lu, Z., Lu, X, Lu, W., y Masri, S. F. (2012). Experimental studies of the effects of buffered particle dampers attached to a multi-degree-of-freedom system under dynamic loads, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 331, 2007–2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2011.12.022
Lu, Z., Wang, D., y Li, P. (2014). Comparison study of vibration control effects between suspended tuned mass damper and particle damper. Shock and Vibration, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/903780
Lu, Z., Wang, D., Masri, S. F., y Lu, X. (2016). An experimental study of vibration control of wind-excited high-rise buildings using particle tuned mass dampers. Smart Structures and Systems, 18(1), 93–115. http://dx.doi.org/10.12989/sss.2016.18.1.093
Lu, Z., Chen, X., Zhang, D., y Dai, K. (2017). Experimental and analytical study on the performance of particle tuned mass dampers under seismic excitation. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 46(5), 697-714. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.2826
Lu, Z, Wang, Z, Masri, SF, y Lu, X. (2018a). Particle impact dampers: Past, present, and future. Struct Control Health Monit; 25:e2058. https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2058
Lu, Z., Chen, X., y Zhou, Y. (2018b). An equivalent method for optimization of particle tuned mass damper based on experimental parametric study. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 419, 571-584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2017.05.048
Lu, Z., Masri, S. F., y Lu, X. (2020). Particle damping technology based structural control. Springe, ISBN 978-981-15-3498-0.
Lu, Z., Zhang, J., Wang, D. (2021). Energy analysis of particle tuned mass damper systems with applications to MDOF structures under wind-induced excitation. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 218, 104766, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104766
Masri, S. F., y Ibrahim, A. M. (1973). Response of the impact damper to stationary random excitation. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 53(1), 200-211. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1913319
Monsalvo, I. (2019). Efectos de los amortiguadores de masa sintonizada en la respuesta sísmica de estructuras de la Ciudad de México, Tesis maestría, Instituto de Ingeniería UNAM.
Naeim, F., et al. (2011). Performance of tall buildings in Santiago, Chile during the 27 February 2010 offshore Maule, Chile earthquake. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 20 (1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/tal.675
Ogawa, K., T. Ide, y T. Saitou. 1997. Application of impact mass damper to a cable-stayed bridge pylon. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics 72 (1–3), 301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-6105(97)00265-1
Papalou, A. y Masri, S.F. (1996). Performance of particle dampers under random excitation, J. Vib. Acoust. T- ASME. 118(4), 614-621. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2888343
Papalou, A. y Strepelias, E. (2014). Effectiveness of particle dampers in reducing monuments’ response under dynamic loads, Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct., 23 (2),128-135. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2014.943913
Petersen, N.R. (1980). Design of large scale tuned mass dampers, Struct. Control, 581-596.
Sánchez, M., y Carlevaro, C. M. (2013). Nonlinear dynamic analysis of an optimal particle damper. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 332(8), 2070-2080.
SAP2000 (2016). Computers and Structures, Inc. SAP2000 Integrated Software for Structural Analysis and Design, Version 17.2.0*. Berkeley, CA: Computers and Structures, Inc.
Sims, N.D., Amarasinghe, A. y Ridgway, K. (2005). Particle dampers for workpiece chatter mitigation, Manuf. Eng., 16(1), 825-832. https://doi.org/10.1115/IMECE2005-82687
Soto‐Brito, R., y Ruiz, S. E. (1999). Influence of ground motion intensity on the effectiveness of tuned mass dampers. Earthquake engineering & structural dynamics, 28(11), 1255-1271. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9845(199911)28:11%3C1255::AID-EQE865%3E3.0.CO;2-C
Teran‐Gilmore, A., y Jirsa, J. O. (2007). Energy demands for seismic design against low‐cycle fatigue. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 36(3), 383-404. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.663
Vickery, B.J., Davenport, A.G. y Wargon, C. (1970), An investigation of the behaviour in wind of the proposed centrepoint tower in Sydney, Australia, Boundary Layer Wind Tunnel Laboratory, Faculty of Engineering Sciences, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada.
Yan, W., Wang, B., y He, H. (2020). Research on damping mechanism and parameter analysis of particle damper based on energy theory. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 146(6), 04020054. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001772
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Earthquake Engineering

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.





